120
Contenido disponible en
www.neumologia-pediatrica.clREFERENCIAS
1. Carrillo R. Síndrome hepatopulmonar (monografía). Rev Fac Med
UNAM 2001; 44: 207-11.
2. Palma D. The hepatopulmonary Syndrome. J Hepatol 2006; 45:
617-25.
3. Noli k. Prevalence of hepatopulmonary syndrome in children.
Pediatrics 2008; 121: e522-7.
4. Zagolín M. Síndrome hepatopulmonar e hipertensión porto-
pulmonar: dos entidades a diferenciar. Rev Chil Enf Respir 2008;
24: 291-303.
5. Kennedy TC. Exercise aggravated hypoxemia and orthodeoxia in
cirrhosis. Chest 1977; 72: 305-9.
6. Muñoz S. Síndrome hepatopulmonar. Revista Hospital Clínico
Universidad de Chile 2006; 17: 229-37.
7. Arguedas MR. Utility of pulse oximetry screening for hepatopul
monary syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007; 5: 749-54.
8. Rodríguez-Roisin R, Pulmonary-Hepatic Vascular Disorders. Eur
Respir J 2004; 24: 861-80.
9. Rovira Amigo S. Síndrome hepatopulmonar en niños: evaluación y
tratamiento. An Pediatr 2009; 71: 224-9.
10. Najafi M. Effect of oral garlic in children with hepatopulmonary
syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12: 2427-31.
11. Tumgor G. Childhood cirrhosis hepatopulmonary syndrome and
liver transplantation. Pediatr Transplant 2008; 12: 353-7.
12. Willis AD. Hepatopulmonary syndrome in children is conventional
liver transplantation always needed? Clin Transplant 2010 DOI:
10.1111/j.1399-0012.2010.01378.x
13. Alonso Martínez JL. Síndrome hepatopulmonar: mayoría de edad
clínica. Med Clin 2008; 130: 95-7.
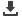
Figura 5.
TC abdomen: cirrosis multinodular, HTP y
esplenomegalia.
Neumol Pediatr 2013; 8 (3): 116-120.
Síndrome hepatopulmonar en pediatría - Maggiolo J. et al